Phonemic Tagging with CELEX
If you have access to the CELEX lexical database, you can integrate LaBB-CAT with it, allowing you to annotate words in your transcripts with data from CELEX - that can include:
- standard phonemic transcriptions - e.g. “difference” → “dɪfrəns” or “dɪfərəns”
- morphological information - e.g. “difference” → “different+ence”
- possible syntactic category - e.g. “difference” → “N”
- frequency data
- lemma
- syllable count
If you want to do force-aligment (to determine the start and end times of each phone within each word), you will need to start with standard phonemic transcriptions, which CELEX can provide.
CELEX is essentially a lexical database, available in English, German, and Dutch. You can purchase the database from the LDC, who provide a number of text files for each language. Once you’ve got these data files, you need to install LaBB-CAT’s CELEX layer manager, which loads the data from the text files into the LaBB-CAT database, and provides mechanisms for generating annotation layers from it.
The basic steps are:
- Buy CELEX from the LDC.
- Save the data files on the same computer than LaBB-CAT is installed on. If you have zip files, these must be unzipped.
- Install the CELEX English layer manager (or the German one if your data is in German), providing the location of the files you saved in the previous step
- Create a new word layer, managed by the CELEX English (or German) layer manager, to generate the annotations you want.
1. Getting CELEX
The CELEX lexical databases are available from the Linguistic Data Consortium (LDC), and are available for English, German, and Dutch. Currently integration with only the English and German databases is supported by LaBB-CAT.
You can buy the databases online from the LDC catalogue.
2. Saving the data files
For each language, the database you receive from the LDC consists of a collection of plain text files, arranged in a set of folders. For the language you are going to install, these files, in their original folders, must be saved on to the same computer that the LaBB-CAT server is running on.
For example, if you’re going to install the English CELEX data, then you need to end up with a folder on your LaBB-CAT server called ENGLISH, which contains the folders called:
- ECT
- EFL
- EFS
- EFW
- EML
- EMW
- EOL
- EOW
- EPL
- EPW
- ESL
Each of these subfolders will contain a file named after the subdirectory (e.g. in the ECT folder there’s a file called ECT.CD) and a file called README.
It doesn’t matter where the top level ENGLISH folder is saved, except that:
- it must be accessible to the LaBB-CAT application (so don’t save it in a private or read-protected location)
- you have to know the path to the folder - e.g. if you’re using a Windows computer, and you save the ENGLISH folder on the C: drive inside a folder called Temp, then the path would be C:\Temp\ENGLISH
3. Installing the layer manager
The CELEX English (or CELEX German or CELEX Dutch) layer manager is a LaBB-CAT module that handles the integration with the CELEX database. It does two tasks:
- When you install the layer manager, it reads all of the data from the CELEX files, and loads it into a relational database that is part of LaBB-CAT (So once you’ve installed the layer manager successfully, you can delete the original CELEX files if you want to, as LaBB-CAT doesn’t need them any more).
- After installation, the layer manager handles looking up relevant data from its database, and using it to generate annotations for words.
To install the layer manager:
- In LaBB-CAT, select on the layer managers link on the menu.
- At the bottom of the page, follow the List of layer managers that are not yet installed link.
- Look for CELEX English (or CELEX Dutch or CELEX German, depending on your needs) and press its Install button.
- You will see a form that asks for some information. Mostly the values are already filled in, and you can leave the default values as they are. The one important field you must specify is the ENGLISH data folder (or GERMAN data folder). You must fill in the path to the folder here. For example if you’re using a Windows computer, and you saved the ENGLISH folder on the C: drive inside a folder called Temp, then the path you enter here should be
C:\Temp\ENGLISH - Click Install Layer Manager.
- During the installation, you will see a progress bar, and information about the files currently being loaded from the CELEX folders. This may take a few minutes. Once it’s finished, the CELEX Layer Manager help page will appear, telling you what to do next (or you can navigate back to this page, and follow the instructions below).
4. Generating annotations
The CELEX layer manager can be configured to annotate word tokens in your transcripts with data found in the CELEX database. As these annotations are about individual words, the layer manager can be used for ‘word layers’ (only).
To create a new layer with CELEX annotations:
- Select on the word layers menu option.
- The row of headers at the top of the list is also a form you can fill in to add a new layer.
Fill in the following details:- Layer ID: Enter a descriptive label - e.g.
phonemes - Type: Phonological
- Manager: CELEX English (or CELEX German or CELEX Dutch)
- Alignment: None (as these are simply tags on the orthographic words)
- Generate: Always
- Description:
All possible phonemic transcriptions of each word, according to the CELEX lexicon, encoded using DISC symbols*
- Layer ID: Enter a descriptive label - e.g.
- Press the New button to create the layer.
You will see a form that allows you to specify what the layer should generate.
- Select the Phonology option on the left to generate phonemic transcriptions.
- Tick the Pronounce Event Override option; this means that if a particular token is annotated on the pronounce layer, that annotation will take precedence over any pronunciation that might be found in CELEX.
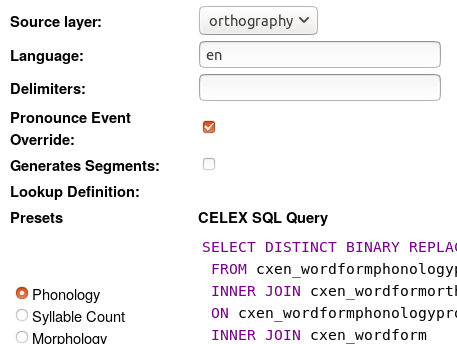
- Press Save
- Press Renegerate
LaBB-CAT will then generate annotations for all the transcripts you already have in your database. If you have a lot of data, this may take a while.
From now on, when you upload a new transcript, the CELEX annotations will automatically be generated for it.
Incomplete words and hesitations
Sometimes speakers start saying a word but don’t finish it. The CELEX layer manager includes some special handling for these case, so that it’s possible to tag them with a pronunciation even though the complete word is not uttered.
- For a hesitation for which multiple syllables are uttered, these can be transcribed up to the point the speaker stops, and then a tilde
~is used to indicate the word was cut off. Then the pronunciation of the word can be manually entered on the pronounce layer, and it will be copied to the CELEX layer as long as the Pronounce Event Override option is ticked.
e.g. if you are using ELAN or Praat for transcripts, you can provide pronounce tags in square brackets, directly after the word with no intervening whitespace, directly in the transcript:
hesi~[hEz@].
If you are using Transcriber for transcripts, Transcriber has a mechanism for adding pronunciations to word tokens; just use that. - For very short hesitations, where only one or teo sounds are uttered, simply transcribing a couple of letters followed by a
~is often sufficient; for such very short hesitations, the CELEX Layer Manager will provide a likely pronunciation. e.g.
he~